Productivity Scenarios and Strategies
As presented in the previous episode, the main concern of the board of directors is to show the clear direction towards which the company must go in the future, namely to establish the company’s productivity vision (or whatever the company wants to be). The senior managers must be constantly concerned with developing the company’s productivity mission (or why the company even exists and what real production capacity it has to ensure), establish the business principles on which to develop the company’s values and establish productivity core business goals in the short, medium and long term and profitability and productivity scenarios and strategies to meet the vision set out by the board of directors. Then middle managers and lower managers should lay down in detail the profitability and productivity strategies and policies (targets and means) in order to fulfill the vision by continuously fulfilling the productivity core business goals.
Productivity goal basic thinking aims at conceiving and continuously developing a manufacturing system to ensure:
-
the required speed of manufacturing, delivery and design of new products,
-
an acceptable cost for manufacturing, for the entire supply chain of existing products and for designing new products,
-
an acceptable quality, and
-
a creativity and involvement of all people within and outside the company to continuously support culture to improve productivity (including quality).
Going further to the perennial needs of any company, profitability and productivity scenarios and strategies, more exactly the multiannual and annual manufacturing profit plan require a continuous synchronization between:
-
target product volumes to be achieved and sold (to ensure target market share) and
-
target productivity required.
In this context, the main challenges of managers that have an impact on the necessary productivity level, and thus on the profit plan aim at:
-
dominating successive changes in the real needs of customers (new profitable products) and technologies by promoting a culture of continuous innovation;
-
ensuring the link between the internal and external environment of the company and continuous identification and addressing sync mismatch through an effective productivity culture at the shop floor level;
-
continually becoming aware of the actual company’s current position and to continuously demonstrate their leadership skills.
The figure below shows Productivity Business Model (PBM) – the basic framework for the development of the MCPD system. As you can see, after defining the Vision and the Mission of Productivity (a topic approached in the previous episode), Productivity Core Business Goals (PCBG) (III), Profitability and Productivity Scenarios (IV) and Profitability and Productivity Strategies (V) are addressed (the three topics of this episode).
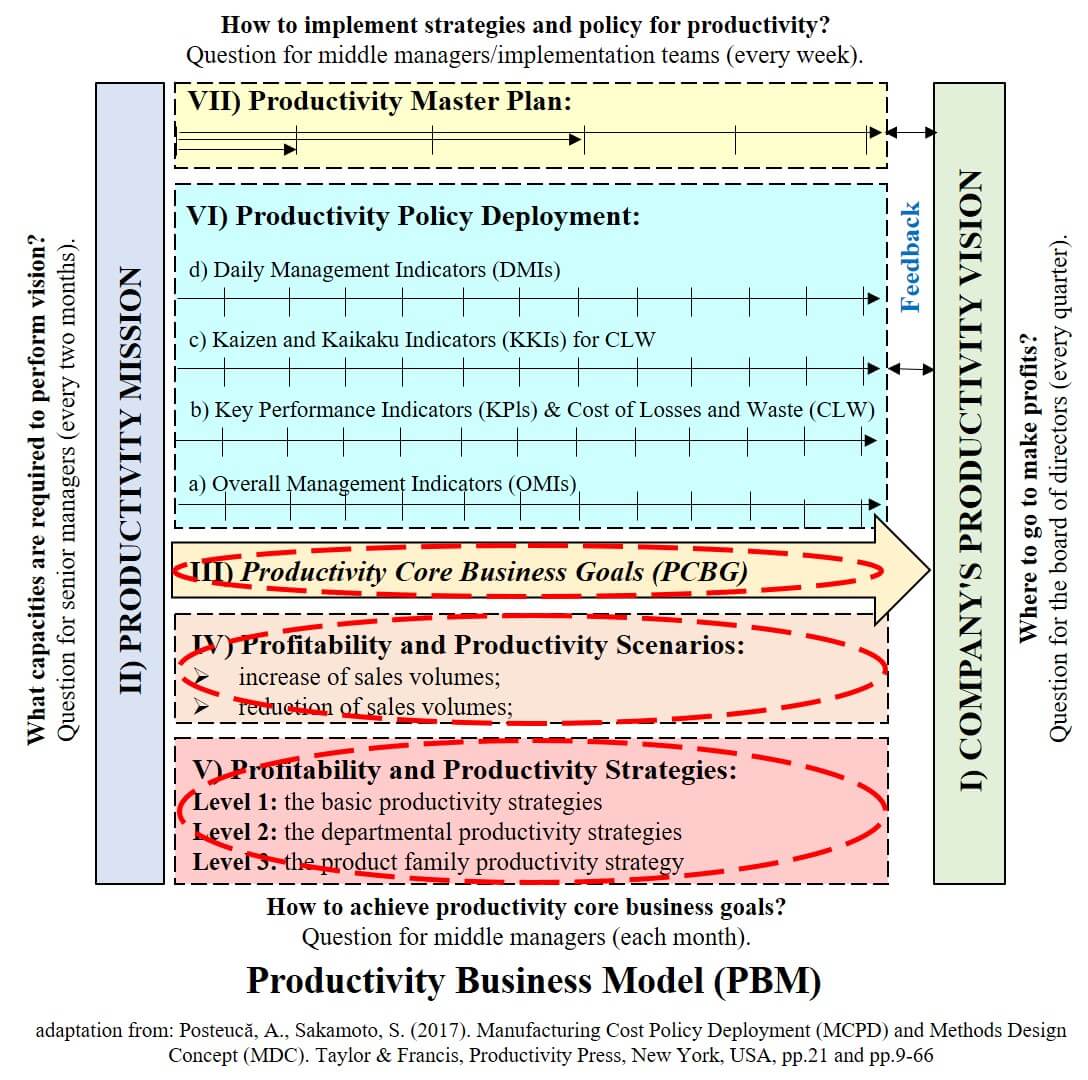
(I) Productivity Core Business Goals (PCBG)
Detailing the productivity mission, in conditions of overcapacity, undercapacity or undercapacity with a hidden overcapacity, is done through the establishment of productivity core business goals (PCBG) in dynamics for the next 3-5 years, based on previous results, to perform quantitative and profit vision. So by PCBG the answer to the question is looked for: How to perform the productivity mission in terms of sales volumes increase or decrease?
Defining and detailing productivity core business goals (PCBG) for Company Productivity Missions detailed with the help of Multiannual Profitability and Productivity Scenarios and Strategies is the top management task that and involves establishing the methods of:
-
manufacturing profit increase,
-
increasing the number of products sold (in manufacturing and all supply chain; improving the mix of existing products – developing products perceived as unique by customers; quality increase – increasing customer satisfaction and increasing quality product ratio),
-
manufacturing cost decrease (reducing costs behind losses and waste or Cost of Losses and Waste – CLW),
-
increasing the morale of all employees, and last but not least,
-
increasing safety and health.
Manufacturing profit increase involves establishing the multiannual dynamics of annual contributions to external manufacturing profit obtained from goods sales and internal manufacturing profit from MCI by improving losses related costs (continuous improvement of current capacities; especially equipment) and waste (continuous improvement of stock levels, especially of work in process – WIP).
(II) Multiannual Profitability and Productivity Scenarios
Starting from declaring the vision of productivity, where a group is working under the guidance of the opinion leaders in the company (the board of directors), namely starting from where the company sees itself in the future (5-10 years) from the productivity mission statement of the company to fulfill its vision under the guidance of senior managers, from PCBG and implicitly, from the prioritization of major courses of action to meet the company vision of productivity, multiannual productivity scenarious develop depending on the state of expected sales growth (undercapacity) or drop in sales (overcapacity).
Achieving the Multiannual Profitability and Productivity Scenarios (for 3-5 years) associated to Company Productivity Missions for each product family cost (PFC) especially for:
– steady increase in sales volumes; the development of scenarios (descriptions of plausible future alternatives) and then strategies (the way of fulfilling a desired future, credible assumptions of a scenario, by planning and mobilizing all necessary resources efficiently and effectively) such as:
-
increasing sales in certain markets of different geographical regions or countries;
-
increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty;
-
increasing the value of the company’s assets;
-
increasing current and future manufacturing capacities;
-
increased synchronization between manufacturing flow and supply chain;
-
increasing manufacturing flexibility;
-
increasing product quality;
-
reducing the time-to-market of new products and supporting product range increase;
-
increasing people’s happiness;
-
increasing people’s creativity and innovation;
-
environmental protection / sustainability,
-
social involvement, etc.;
– decrease of product unit cost of manufacturing; developing scenarios and strategies such as:
-
decreasing material costs;
-
decreasing transformation costs,
-
decreasing design cost,
-
decreasing depreciation costs.
(III) Multiannual Profitability and Productivity Strategies
Therefore, the need for a long-term profitability and productivity strategy is regardless of the internal environment and especially outside the company, especially for thestates of overcapacity or undercapacity with a hidden overcapacity, which are the most common.
Depending on the specifics of the company and its present and future status, Multiannual Profitability and Productivity Strategies are being developed and implemented for 3-5 years associated to Multiannual Profitability and Productivity Scenarios for each product family cost (PFC) for:
-
Level 1: the basic productivity strategies – from the perspective of Cost of Losses and Waste – CLW;
-
Level 2: the departmental productivity strategies;
-
Level 3: the product family productivity strategy;
Therefore, the monthly central question of middle managers on profitability and productivity strategies is: How to meet PCBG? The big challenge of this question is keeping the interest for productivity continuous improvement for everyone in the company, especially for middle managers, lower managers, team leaders and the operators. In order to keep this constant care for productivity, PBM addresses productivity strategies at three interrelated levels.
Therefore, to achieve multiannual manufacturing profits or manufacturing profits goal, multiannual profit scenarios and strategies are required to be developed through the development of multiannual basic productivity strategies in order to:
-
ensure an acceptable level of effectiveness to achieve the annual and multiannual target number of units to be manufactured and sold (by maximize outputs; reduce not effectively used input – losses improvement);
-
ensure an acceptable level of efficiency to achieve the annual and multiannual manufacturing target cost (by minimize inputs; reduce excess amount of input – waste improvement).
Therefore, PCBG and Multiannual Profitability and Productivity Scenarios and Strategies aim to tackle stringent problems/ constraints of productivity. For example, for multiannual productivity strategies to increase synchronization between manufacturing flow and supply chain for a particular product family cost (PFC), PCBGs can be set up such as:
-
reducing manufacturing lead time for each main process;
-
reducing the number of workstations;
-
reducing the cycle time;
-
reducing the setup and transfer time;
-
reducing the factory lead time;
-
reducing the supply lead time and
-
reducing the delivery lead time.
The expected impact concerns the development and then the implementation of objectives, scenarios, strategies and policy (targets and means) of profitability and productivity in a clear and acceptable way by the company and beyond. Based on the objectives and policies, a master plan is developed for implementing the actions and activities needed to achieve the outputs level of performance required to continuously satisfy the corporate vision. In the design, implementation and verification of results of the actions and activities of the productivity master plan all employees are involved: senior managers, middle managers, lower managers and implementation teams of improvements and problem solving that include team leaders and operators.
These latter topics will be addressed in the next episode of our MCPD tutorial.






 English
English Romana
Romana